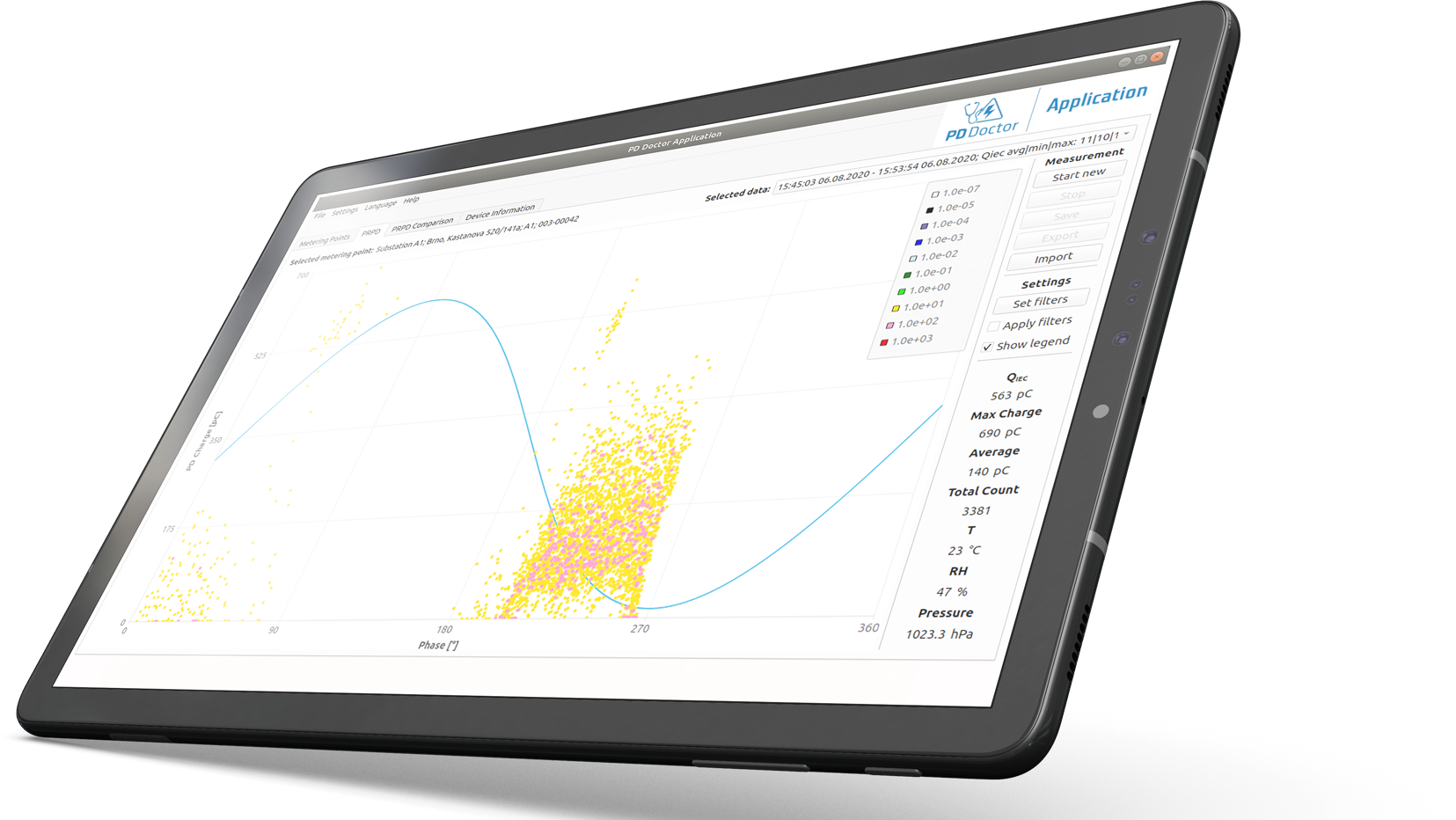
Mi az a részleges kisülés?
A részleges kisülés (PD) az elektromos meghibásodás egy olyan típusa, amely akkor következik be, amikor a két vezető közötti szigetelésnek csak egy része sérül meg. Ez az elektromos áram helyi növekedését eredményezi, ami károsíthatja a környező szigetelést. A részleges kisülés bármilyen típusú elektromos berendezésben előfordulhat, de leggyakrabban a nagyfeszültségű berendezésekben, például transzformátorokban, generátorokban és kábelekben fordul elő.
A részleges kisülést számos tényező okozhatja, többek között gyártási hibák, környezeti tényezők és elektromos feszültség. Ha nem ellenőrzik, a részleges kisülések a berendezés idő előtti meghibásodását okozhatják.
Hogyan mérik a részleges kisülést?
A részleges kisülés többféle módszerrel is mérhető, többek között elektromos, akusztikus és optikai módszerekkel. A legelterjedtebb módszer az elektromos mérés, amely érzékelőkkel érzékeli a részkisülés során a szigetelésen átfolyó áramot.
Az akusztikus mérés során mikrofonokat használnak a PD hangjának meghallgatására. Ez a módszer kevésbé elterjedt, de olyan esetekben alkalmazható, amikor az elektromos mérés nem lehetséges.
Az optikai mérés fényt használ a részleges kisülések észlelésére. Ezt a módszert jellemzően nagyfeszültségű berendezéseknél alkalmazzák, ahol az elektromos mérések nem lehetségesek.
Melyek a részleges kisülés típusai?
A PD három alapvető típusa létezik:
- Külső – gázokban az elektródák szomszédságában, kis sugarú vagy nagy görbületű elektródákban.
- Felületi – az elektródák szomszédságában a szilárd és a gáz dielektrikum határán.
- Belső – szilárd vagy folyékony dielektrikummal körülvett gázokban.


Milyen előnyökkel jár a részleges kisülési elemzés?
A részkisülés-elemzés (PDA) – PD Doctor számos előnyt kínál, többek között:
- A problémák proaktív felismerése: A részkisülések megfigyelésével a PDA felismeri a problémákat, mielőtt azok a berendezés meghibásodását okoznák.
- A problémák korai felismerése: A PDA a problémákat korai stádiumukban észleli, amikor könnyebben orvosolhatóak.
- Csökkentett állásidő: A problémák felismerésével és kijavításával, mielőtt azok a berendezés meghibásodását okoznák, a PDA segíthet csökkenteni az állásidőt.
- Javított biztonság: A PDA segíthet javítani az elektromos berendezések biztonságát azáltal, hogy a problémákat még azelőtt észleli és javítja, mielőtt azok meghibásodást okoznának.
- Javított megbízhatóság: A meghibásodások számának csökkentésével a PDA segíthet javítani az elektromos berendezések megbízhatóságát.
Mik a részleges kisüléselemzés korlátai?
A részkisülés-elemzés nem tökéletes diagnosztikai eszköz, és vannak bizonyos korlátai, többek között:
- Hamis pozitív eredmények: Bizonyos esetekben a PD-t az elektromos meghibásodáson kívül más tényezők is okozhatják. Ez hamis pozitív eredményekhez vezethet, ami szükségtelen leállásokat okozhat.
- Az értelmezés nehézségei: A részleges kisülési méréseket nehéz lehet értelmezni, és gyakran szakértői elemzésre van szükség.
- Szakértői elemzést igényel: A PDA gyakran egy szakképzett mérnök szakértelmét igényli a mérések megfelelő értelmezéséhez.
- Bizonyos típusú berendezésekre korlátozódik: A PDA jellemzően csak nagyfeszültségű berendezésekben, például transzformátorokban, generátorokban és kábelekben lehetséges.
“A forgógépek meghibásodásainak 60 százalékát a szigetelés elvesztése és károsodása okozza.“
(Forrás: CIRGE)
Korlátjai ellenére a részleges kisüléselemzés értékes diagnosztikai eszköz, amely segíthet javítani az elektromos berendezések biztonságát és megbízhatóságát. Fontos része a proaktív karbantartási megközelítésnek.
Gyanítja, hogy a berendezése részleges kisüléstől szenved?